The firm and its objectives
The profit- and sales-maximizing outputs are, respectively, OQP and OQ,. Now if, for example, the minimum required profit level is OP\, then the sales-maximizing output OQ, will provide plenty of profit, and that is the amount it will pay the sales maximizer to produce.
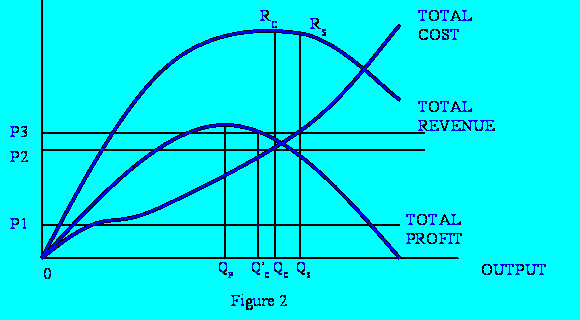
His selling price will then be set at Q,R,/OQ,. But if the producer’s required profit level is OP2, output OQ,, which yields insufficient profit, clearly will not do. Instead, his output will be reduced to level OQC, which is just compatible with his profit constraint.
It will be argued presently that in fact only equilibrium points in which the constraint is effective (OQC rather than OQ,) can normally be expected to occur when other decisions of the firm are taken into account.
The profit-maximizing output, OQP, will usually be smaller than the one which yields either type of sales maximum, OQ, or OQC. This can be proved with the aid of the standard rule that at the, point of maximum profit marginal cost must equal marginal revenue. For marginal cost is normally a positive number (we can’t usually produce more of a good for nothing).